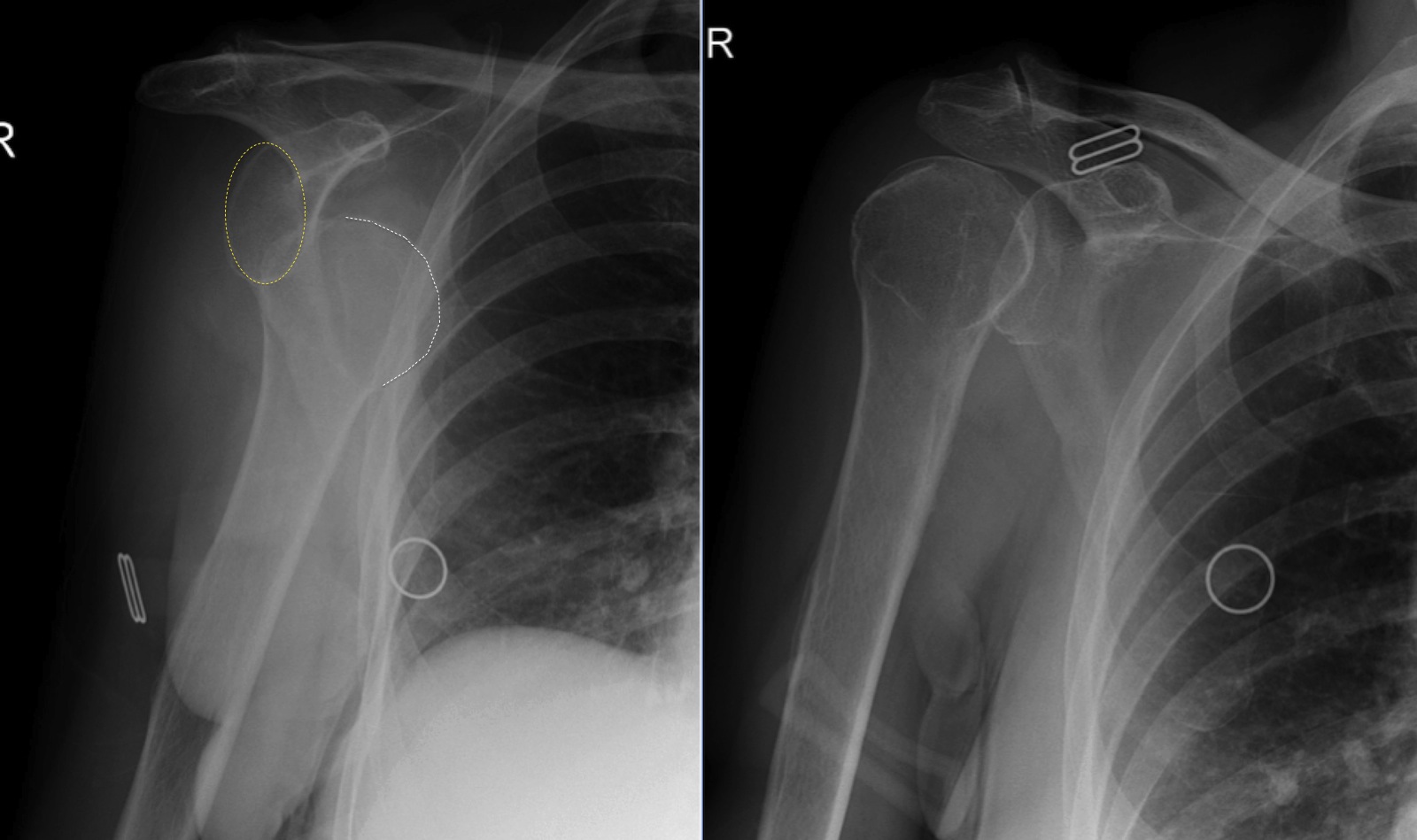
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View . In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations.
from www.vrogue.co
The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa.
Shoulder Dislocation X Ray vrogue.co
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations. The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue.
From mavink.com
Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From www.reddit.com
Another example of the importance of orthogonal views. r/Radiology Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From litfl.com
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation • LITFL • Trauma Library Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa.. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From coreem.net
Shoulder Dislocation Core EM Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From www.embeds.co.uk
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation EMbeds.co.uk Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow),. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From radiopaedia.org
Anterior shoulder dislocation Image Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. This. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From orthopaedicprinciples.com
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation — Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From jetem.org
Anterior Shoulder Dislocation, PreReduction AP XRay, Annotated. JETem Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. In the y. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From www.svuhradiology.ie
Posterior shoulder dislocation Radiology at St. Vincent's University Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa. This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From www.orthobullets.com
Posterior Shoulder Instability & Dislocation Shoulder & Elbow Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. The. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From litfl.com
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation • LITFL • Trauma Library Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View This view eliminates most overlying bony and soft tissue. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From geekymedics.com
Shoulder Xray Interpretation Radiology Geeky Medics Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa.. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From geekymedics.com
Shoulder Xray Interpretation Radiology Geeky Medics Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. In the. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From www.resilienceorthopedics.com
Shoulder Dislocation A Complete Guide Dr Mehta, San Jose Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From www.vrogue.co
Shoulder Dislocation X Ray vrogue.co Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From geekymedics.com
Shoulder Xray Interpretation Radiology Geeky Medics Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. Anterior dislocation will result in the humeral head being displaced deep into the far field (away from one's probe), whereas posterior dislocations. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From orthosho.com
Shoulder Dislocation OrthoSHO Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View The axillary lateral view is the most accurate radiographic image to diagnose a posterior shoulder dislocation. The glenohumeral joint will be widened and the. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of injury, key imaging findings, therapeutic options and associated. What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.
From doccottlesdesk.blogspot.com
Doc Cottle's Desk Posterior shoulder dislocation confirmed by ultrasound Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View What signs do you look for on x ray for this condition?. In the left image (anteroposterior view), the humeral head is internally rotated,. In the y view, lines drawn through the acromion (blue arrow), coracoid (black arrow), and scapular body (red arrow) intersect at the center of the glenoid fossa. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms of. Posterior Shoulder Dislocation X Ray Y View.